Cleaning Up Coal Ash
For well over a century, power plants across the country have burned coal to generate electricity. And for just as long, leftover coal ash has been dumped in open, unlined pits near the power plant, usually located on a river or lake. Every year, U.S. power plants produce 130 million tons of coal ash, which is the second largest waste stream in the country after municipal garbage.
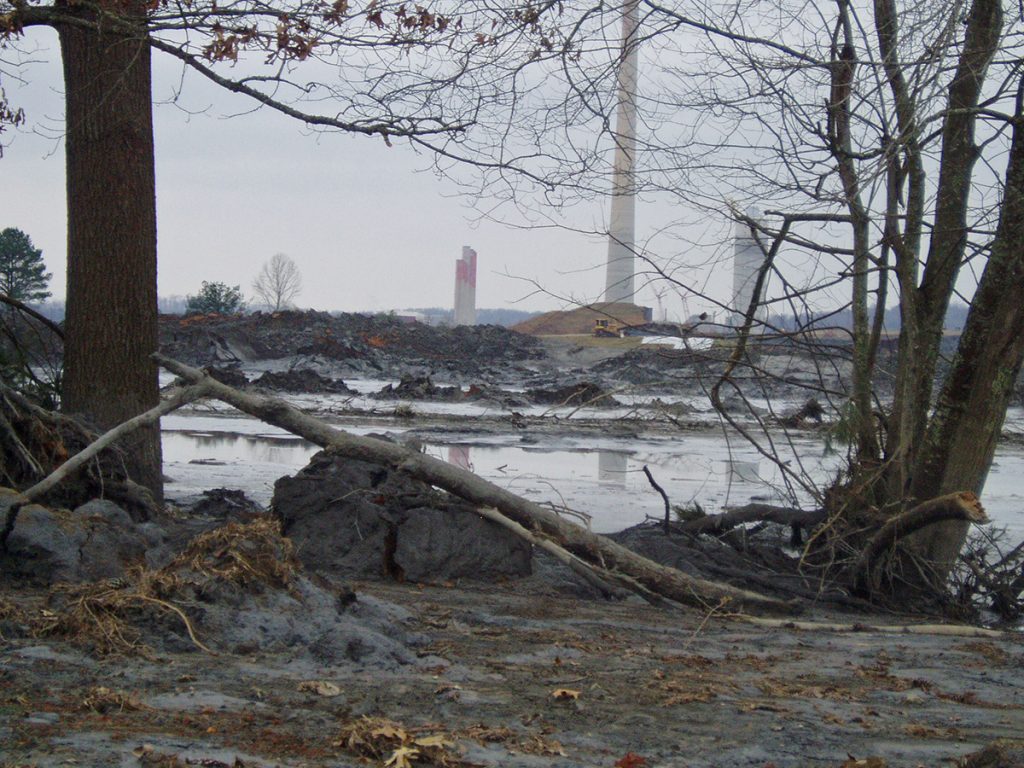
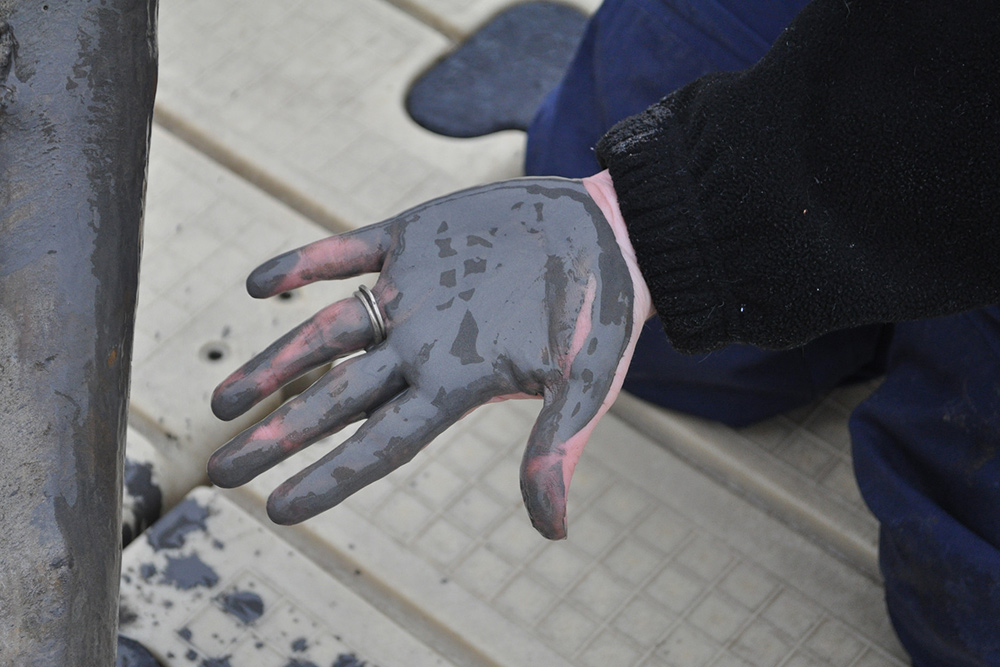
Coal ash concentrates the toxic heavy metals found in coal, including arsenic, mercury, lead and selenium. Stored in unlined, wet impoundments, coal ash has been leaking these toxics into our groundwater and surface waters for years. Sometimes these impoundments collapse — with disastrous results.
Yet government regulations for coal ash management are either non-existent or sparse, and there is little enforcement of the regulations that do exist. In North Carolina, this lack of oversight — and the complicity between state regulators, elected officials and Duke Energy — came to a boiling point in February 2014 when one of Duke’s coal ash impoundments spilled 39 million tons of ash into the Dan River.
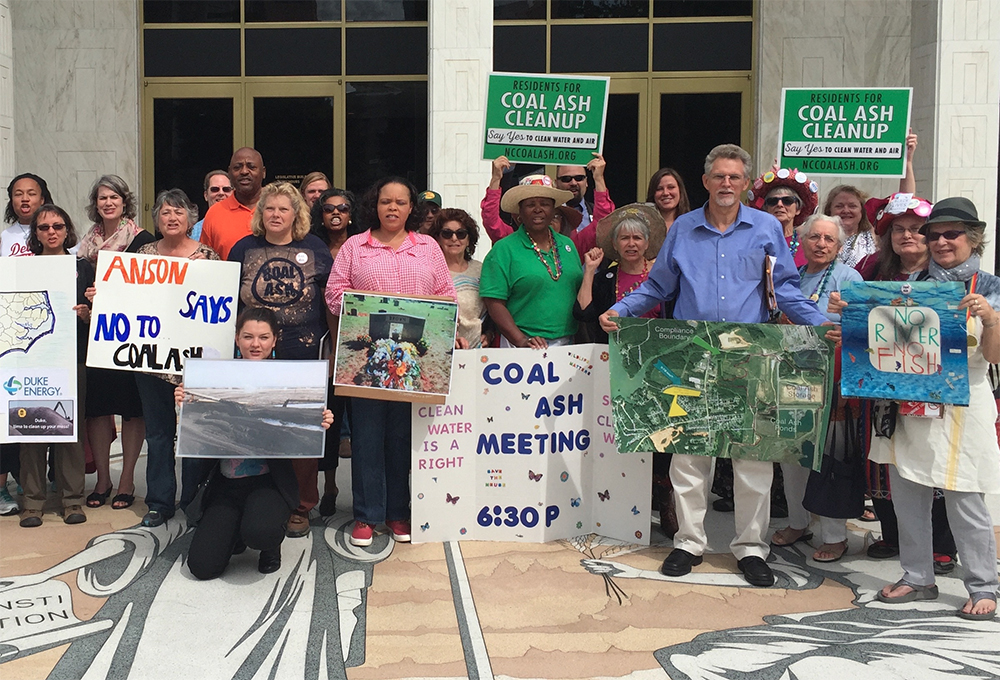
Citizens living near North Carolina’s 33 coal ash impoundments — all of which have leaked — have fought for transparency from Duke and the state, and for cleanup of the pollution that threatens their property value, health and family. Their actions forced this issue into the headlines of news networks and to the forefront of environmental justice conversations in the United States.
Appalachian Voices stood with these communities as we worked for years to compel Duke Energy and the N.C. Department of Environmental Quality to excavate coal ash from all the North Carolina sites and dispose of it either in lined, dry landfills, away from waterways, or by recycling it for concrete or other uses, provided it’s done in a manner that protects public health and the environment.
On Jan. 2, 2020, North Carolina announced a historic settlement with one of the state’s most powerful corporations and polluters, Duke Energy. The settlement requires Duke to move nearly 80 million tons of toxic coal ash at six of its power plants to properly lined landfills onsite or recycle it.

Learn information about specific coal ash impoundments in the South, including health threats and safety ratings:
Additional Resources
Fact sheets, videos, links to academic research, and more
Sign Up to Act
Help us protect the health of our communities and waterways.
Latest News
Virginia Restoration Reroutes Troubled Water
In Rockbridge County, Va., construction vehicles this August began carving out nearly half a mile of new streambed for the Maury River. Tree plantings to stabilize the soil are scheduled to begin this fall. This will be the largest stream restoration project completed by the Virginia Department of Game and Inland Fisheries, which received funding from a federal grant program and a local family farm.
Heavy-Volume Water Pipe Proposed on Nolichucky River in Tennessee
Rights to the Nolichucky River in Midway, Tenn., have remained contentious since 2011, when U.S. Nitrogen proposed an industrial chemical facility with a 10-mile pipeline connected to the river. The pipeline would withdraw nearly 2 million gallons of water per day, and 500,000 gallons would be returned, contaminated with small amounts of ammonium and nitrogen.
Serving Virginia Parks
The Virginia Department of Conservation and Recreation is launching the inaugural year of its Virginia Service and Conservation Corps program. Participants will maintain trails and improve natural habitats at Pocahontas, Leesylvania or Hungry Mother State Park.
A First-Hand Look at Emerging Opportunities in Eastern Kentucky
When eastern Kentucky residents shared their regional vision at Appalachia’s Bright Future Conference this September, they could point to real examples. The main highlight of the conference, which attracted more than 100 people from across Appalachia, was a collection of 20 tours of local businesses, farms, music and art venues, tourist attractions, and community cooperatives.
The Catawba River’s “Pollution Solution”
Keeping doggy waste off the lawn and using eco-friendly fertilizer are gaining ground as efficient approaches to healthy waterways. In North Carolina three ninth-grade students developed a curriculum to teach their peers these practices.
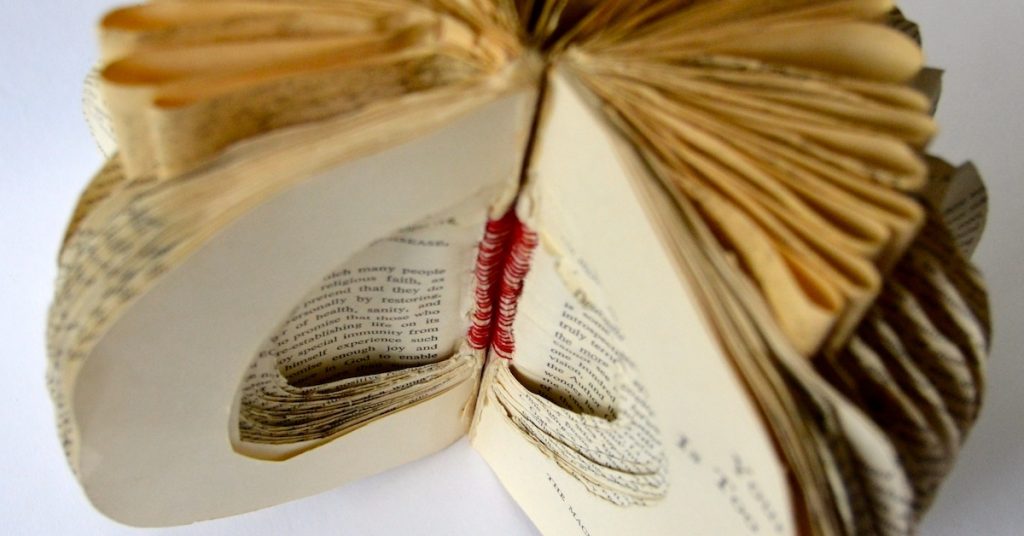
One Artist’s Experience with Coal Ash
Caroline Armijo began an environmental justice art project after seeing many friends and family die from cancer in her North Carolina community, near one of the state’s largest coal ash impoundments. In this excerpt from her website, she describes the circumstances that shaped her paper sculpture creation, titled “Gray Matter.”