Cleaning Up Coal Ash
For well over a century, power plants across the country have burned coal to generate electricity. And for just as long, leftover coal ash has been dumped in open, unlined pits near the power plant, usually located on a river or lake. Every year, U.S. power plants produce 130 million tons of coal ash, which is the second largest waste stream in the country after municipal garbage.
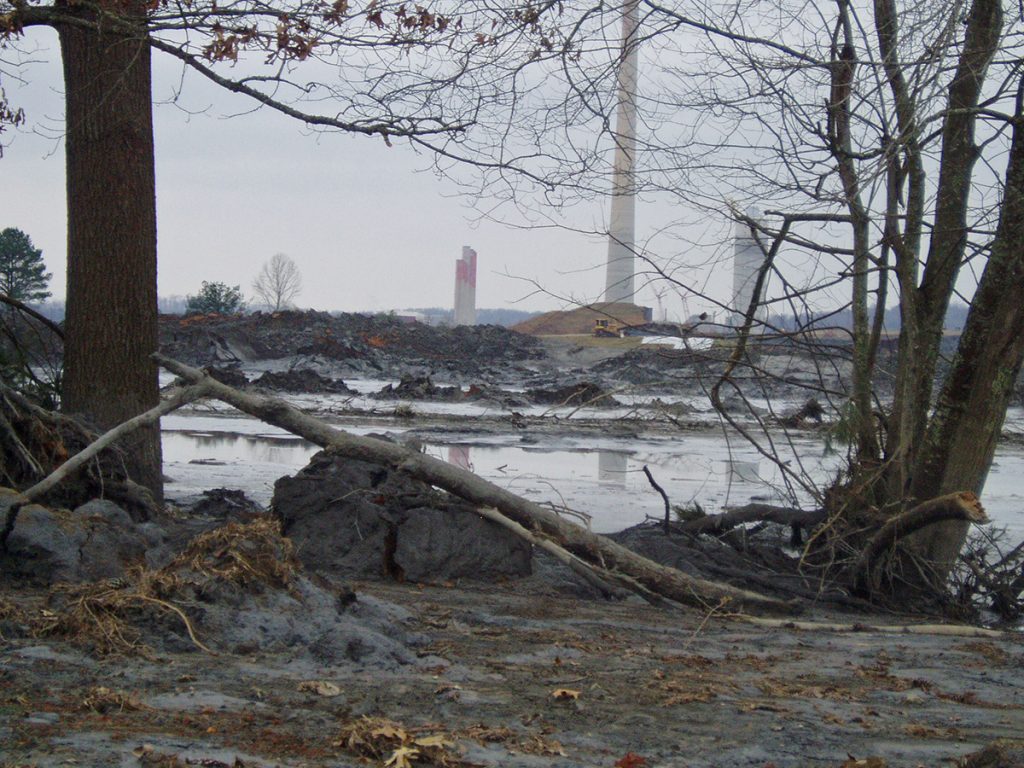
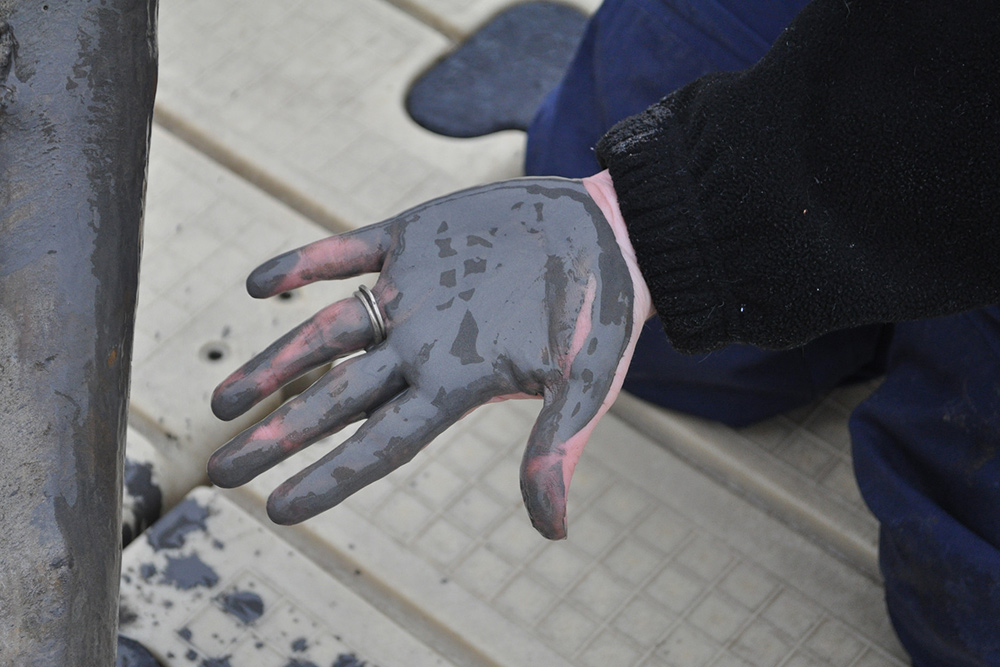
Coal ash concentrates the toxic heavy metals found in coal, including arsenic, mercury, lead and selenium. Stored in unlined, wet impoundments, coal ash has been leaking these toxics into our groundwater and surface waters for years. Sometimes these impoundments collapse — with disastrous results.
Yet government regulations for coal ash management are either non-existent or sparse, and there is little enforcement of the regulations that do exist. In North Carolina, this lack of oversight — and the complicity between state regulators, elected officials and Duke Energy — came to a boiling point in February 2014 when one of Duke’s coal ash impoundments spilled 39 million tons of ash into the Dan River.
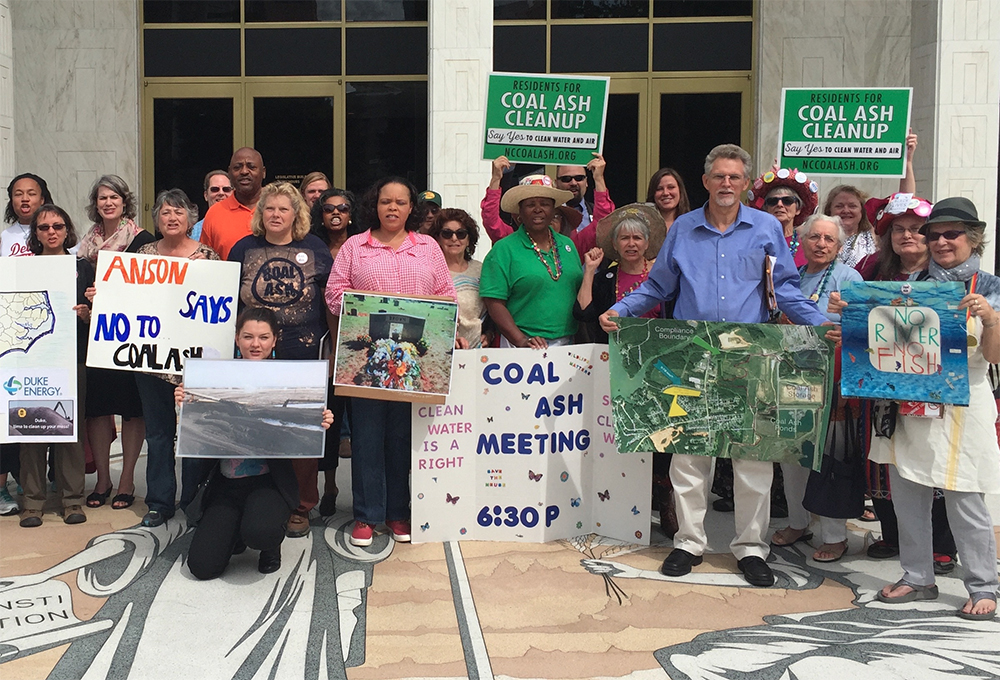
Citizens living near North Carolina’s 33 coal ash impoundments — all of which have leaked — have fought for transparency from Duke and the state, and for cleanup of the pollution that threatens their property value, health and family. Their actions forced this issue into the headlines of news networks and to the forefront of environmental justice conversations in the United States.
Appalachian Voices stood with these communities as we worked for years to compel Duke Energy and the N.C. Department of Environmental Quality to excavate coal ash from all the North Carolina sites and dispose of it either in lined, dry landfills, away from waterways, or by recycling it for concrete or other uses, provided it’s done in a manner that protects public health and the environment.
On Jan. 2, 2020, North Carolina announced a historic settlement with one of the state’s most powerful corporations and polluters, Duke Energy. The settlement requires Duke to move nearly 80 million tons of toxic coal ash at six of its power plants to properly lined landfills onsite or recycle it.

Learn information about specific coal ash impoundments in the South, including health threats and safety ratings:
Additional Resources
Fact sheets, videos, links to academic research, and more
Sign Up to Act
Help us protect the health of our communities and waterways.
Latest News
Cash for Carbon: Working Woodlands Program Grows in Appalachia
Over 25,000 acres of forest in Kentucky, Tennessee and Virginia will remain undeveloped for use in Forest Stewardship Council-certified timber markets.
West Virginia State Park Logging Bill Defeated
Widespread public backlash led to the defeat of a West Virginia bill that would have lifted the 80-year ban on commercial logging in state parks.
Sanctuary for Research Chimpanzees Opens Outdoor Habitat
In January, Georgia-based chimpanzee sanctuary Project Chimps opened a six-acre expanse of woods to 15 apes that had spent their entire lives indoors for biomedical research.
Eastern Cougar Declared Extinct
The eastern cougar, a subspecies of the North American cougar that once roamed much of the Eastern United States and parts of Canada, was officially declared extinct in February.
N.C. Rock Faces Closed to Protect Falcons
The U.S. Forest Service is seasonally closing nine recreational rock faces in North Carolina to protect rare peregrine falcon nests.
East Tennessee Historic Park Wins State Award
The Tennessee Department of Environment and Conservation named the Sgt. Alvin C. York State Historic Park as the 2017 State Park of the Year.