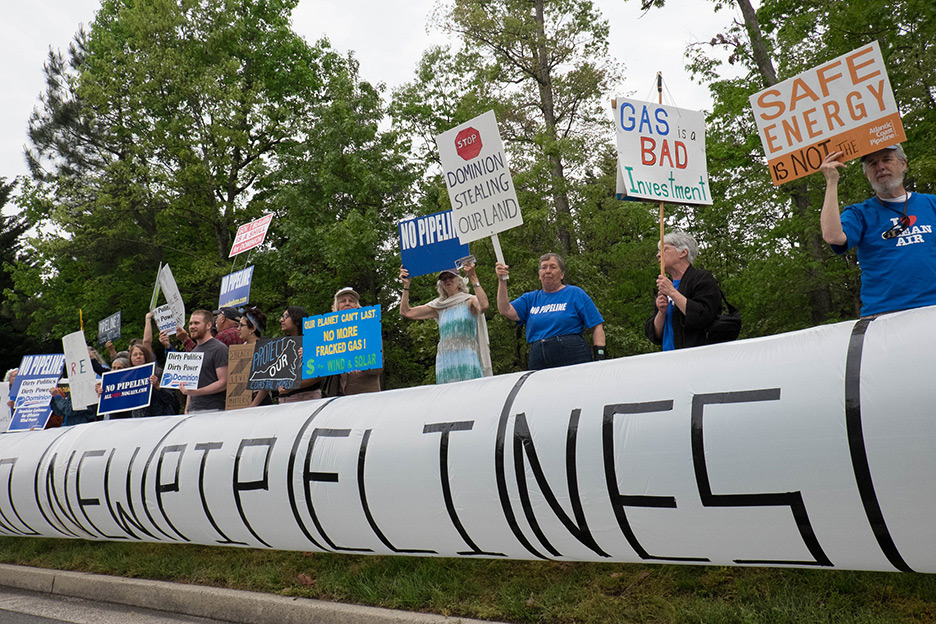
Stop Pipelines & Fracked Gas

Photo By Sierra Shamer / Fractracker
Two decades ago, so-called natural gas exploded on the American energy market, pushed by the industry as a supposedly clean “bridge” fuel to transition the economy from dirty coal to renewable sources of electricity generation like solar and wind.
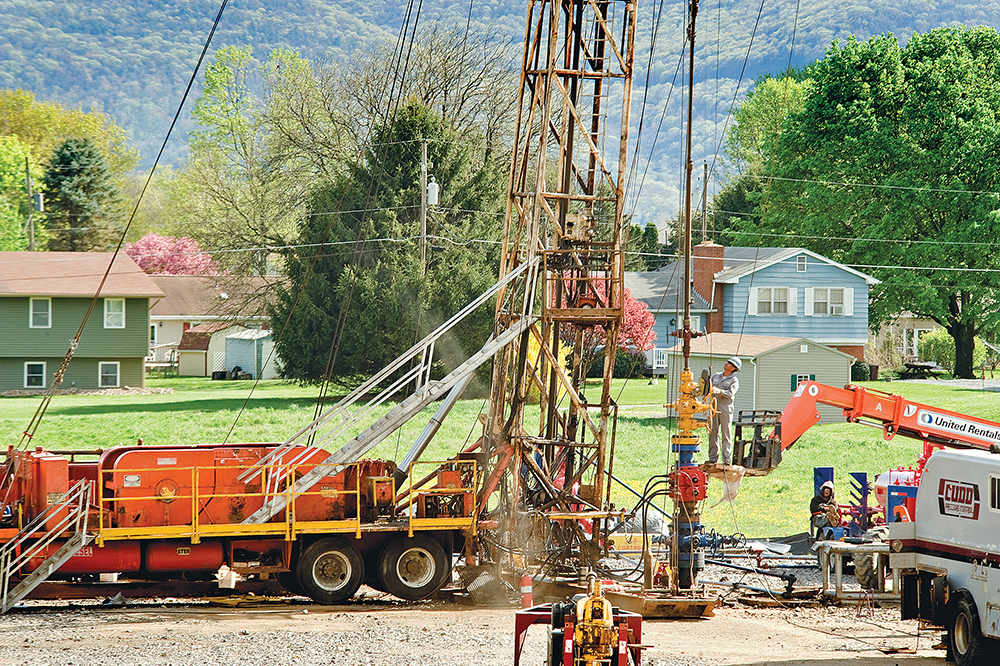
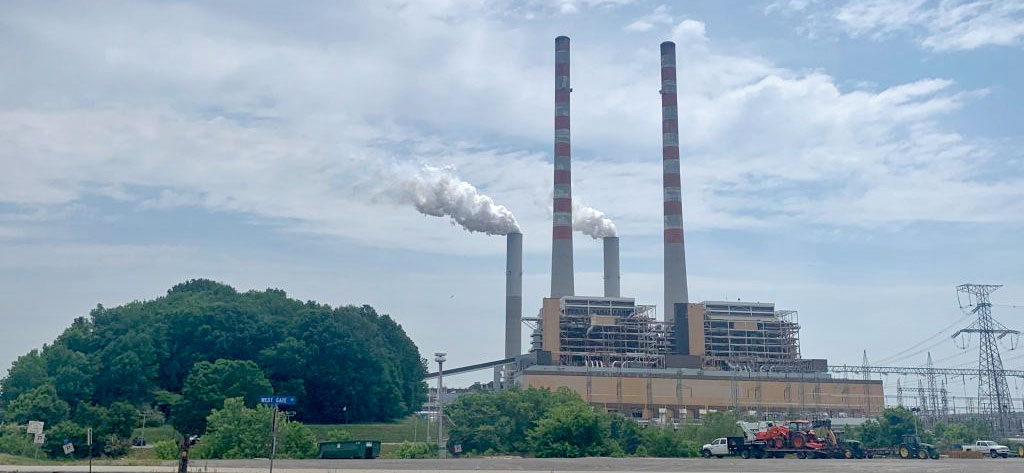
But this gas is far from clean. From the time that it is extracted using a destructive drilling method called fracking, its transport through pipelines, train cars and trucks, to the power plants where it is burned, the dire environmental and human costs of this fossil fuel are now abundantly clear. In particular, this polluting infrastructure is often sited in communities of color, lower-income areas and other environmental justice communities.
Studies show that investments in renewable energy and energy efficiency are on par with, or sometimes more affordable than, building new gas infrastructure. Many states are enacting policies to tap into the rising solar and wind sector. Yet the fossil fuel industry is rushing to build methane gas pipelines and power plants to squeeze as much profit as possible out of the waning fuel, putting most of the financial risk on customers.
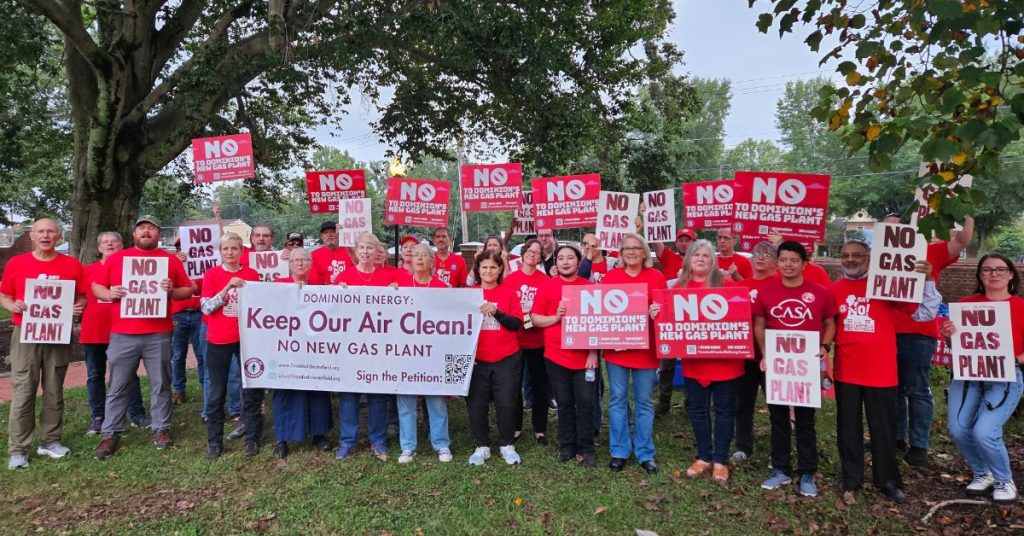
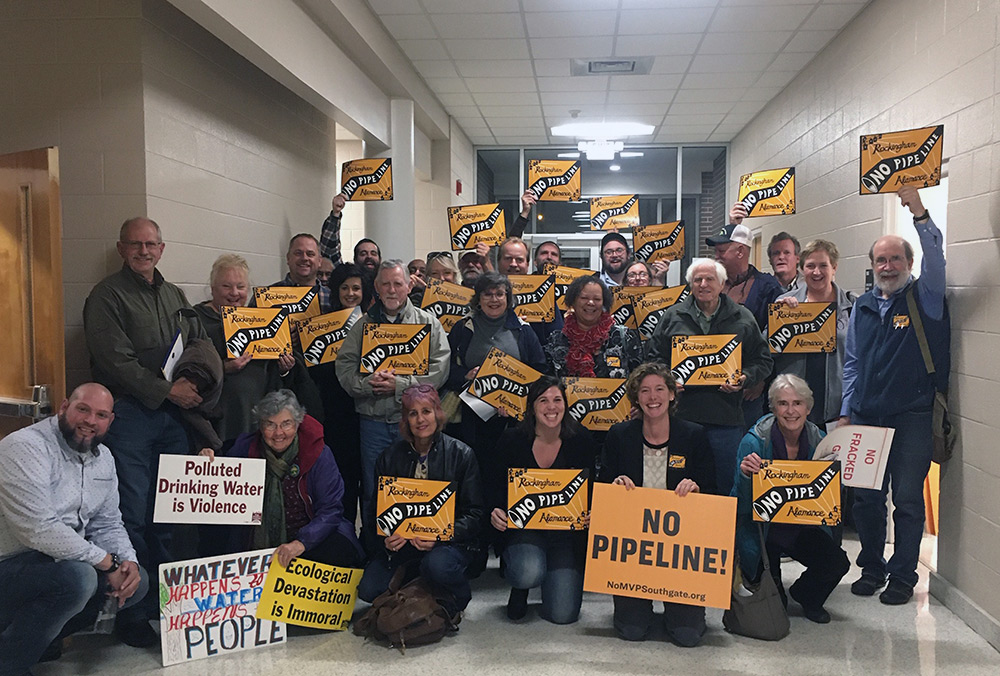
Appalachian Voices is tackling the spread of fracked gas head-on by legally challenging fossil fuel proposals and pushing back against the antiquated policies and rubber-stamping agencies that govern the development of gas infrastructure. We are also partnering with communities in the fight against new fossil fuel infrastructure, providing resources and training to bolster local opposition. And we are pressuring decision-makers to force them to consider the harm to communities threatened by polluting energy development.
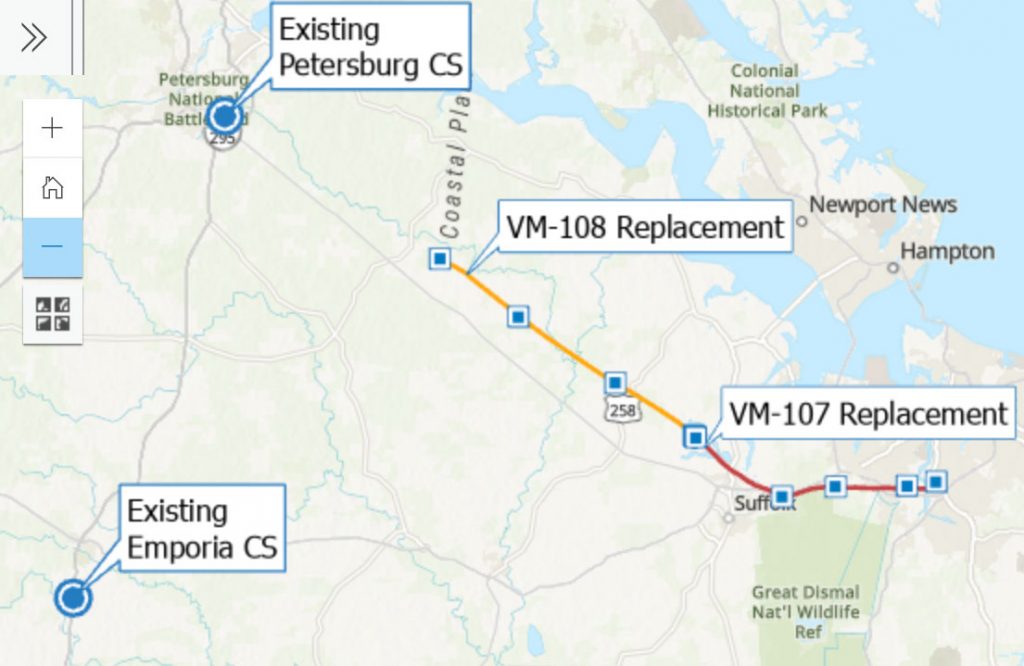
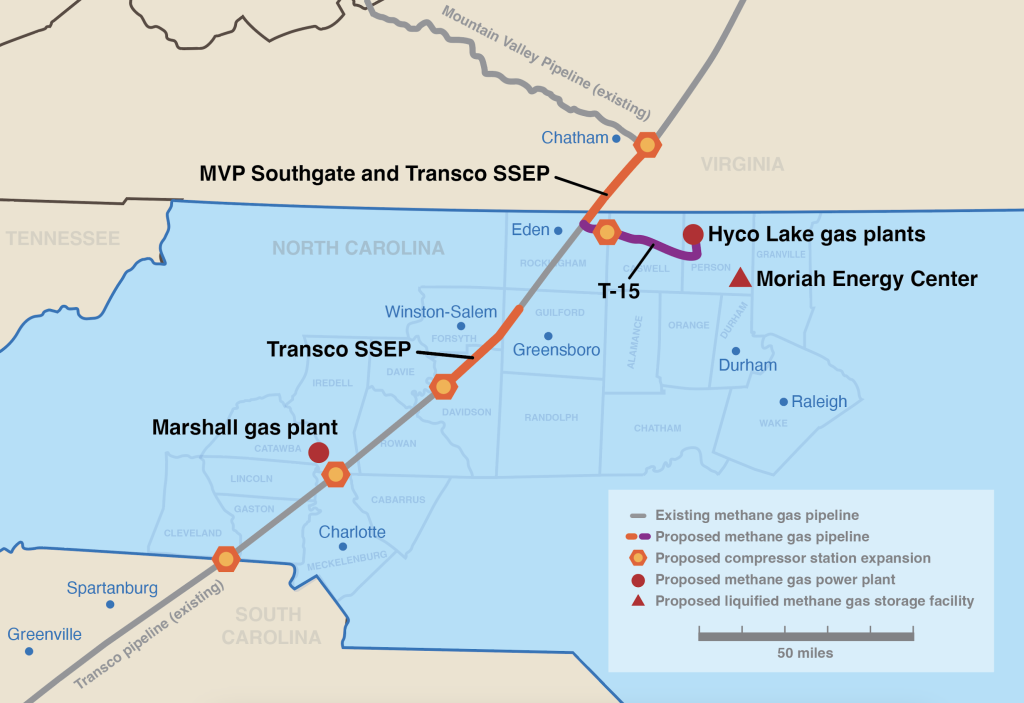
And the tide is starting to turn. In July 2020, Duke Energy and Dominion Energy canceled the 600-mile Atlantic Coast Pipeline. The massive fossil fuel project was riddled with problems, starting with the fundamental fact it was not needed to meet energy demand. Standing beside the many communities and organizations that made this historic victory possible, we’re taking this momentum and applying it toward the fight against other destructive, climate-harming projects that threaten community safety, our clean air and water, and that would raise electricity costs for residents.

Latest News
Atlantic Coast and Mountain Valley Pipelines Struggle to Get Underway
While preliminary tree felling has been approved for the Mountain Valley and Atlantic Coast pipelines, the projects are still being met with staunch resistance from activists and lawmakers alike.
Continuing the Fight Against Pipelines
The pipeline resistance continues on many fronts despite some recent permit approvals for the Atlantic Coast and Mountain Valley pipelines.
With your help, Virginia legislation can protect our water from pipelines
We’ve resisted the Mountain Valley and Atlantic Coast pipelines for more than three years. Now Virginia lawmakers need to hear our voices to ensure that legislation to better protect landowners and water resources from fracked-gas pipelines becomes law.
Va. bill on electric rates a bad deal for consumers
CONTACT: Cat McCue, Communications Director, cat@appvoices.org, 434-293-6373 The…
Controversy in Va. mounts as Dominion bill nears a vote
Dominion Energy is at it again, using its political influence to push legislation that would weaken regulatory oversight and boost profits at the expense of its Virginia customers. But this time something is different. The corporate giant is being met with significant opposition.