Cleaning Up Coal Ash
For well over a century, power plants across the country have burned coal to generate electricity. And for just as long, leftover coal ash has been dumped in open, unlined pits near the power plant, usually located on a river or lake. Every year, U.S. power plants produce 130 million tons of coal ash, which is the second largest waste stream in the country after municipal garbage.
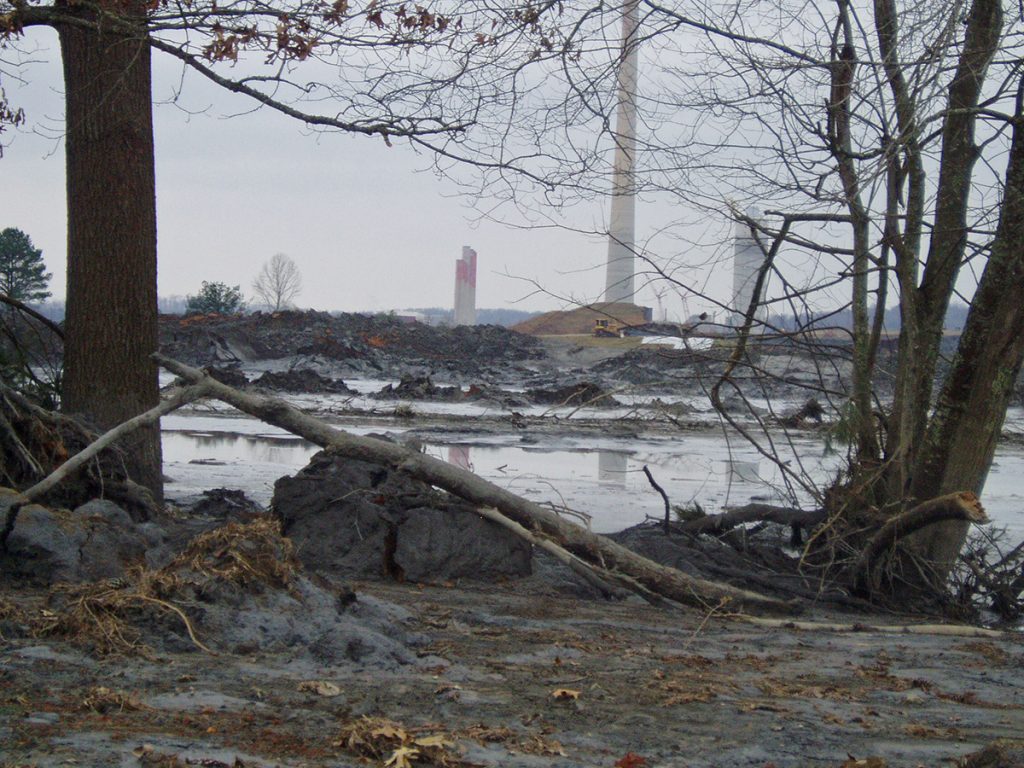
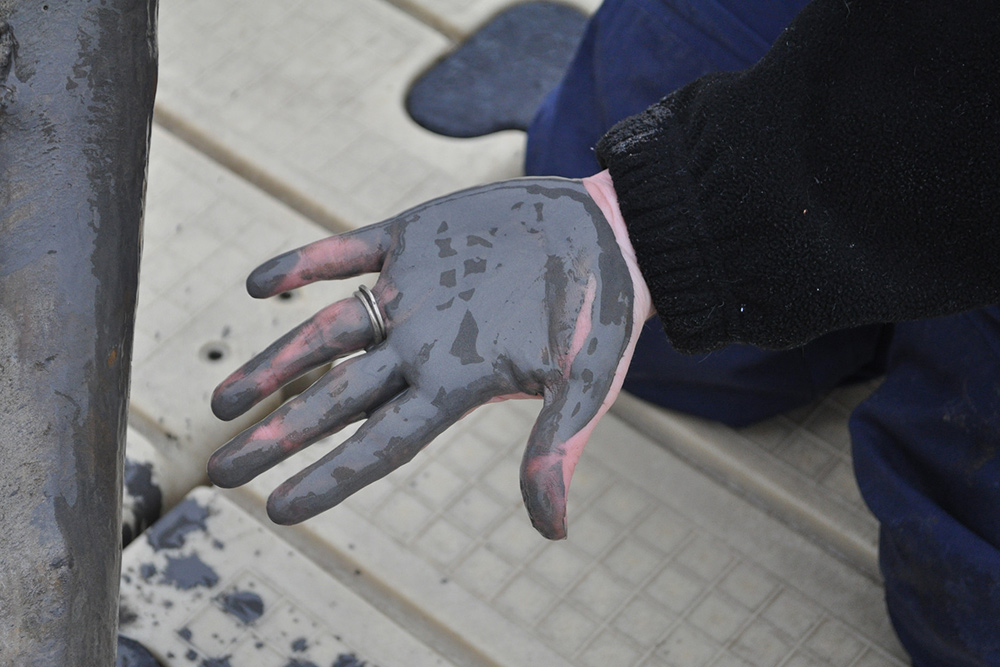
Coal ash concentrates the toxic heavy metals found in coal, including arsenic, mercury, lead and selenium. Stored in unlined, wet impoundments, coal ash has been leaking these toxics into our groundwater and surface waters for years. Sometimes these impoundments collapse — with disastrous results.
Yet government regulations for coal ash management are either non-existent or sparse, and there is little enforcement of the regulations that do exist. In North Carolina, this lack of oversight — and the complicity between state regulators, elected officials and Duke Energy — came to a boiling point in February 2014 when one of Duke’s coal ash impoundments spilled 39 million tons of ash into the Dan River.
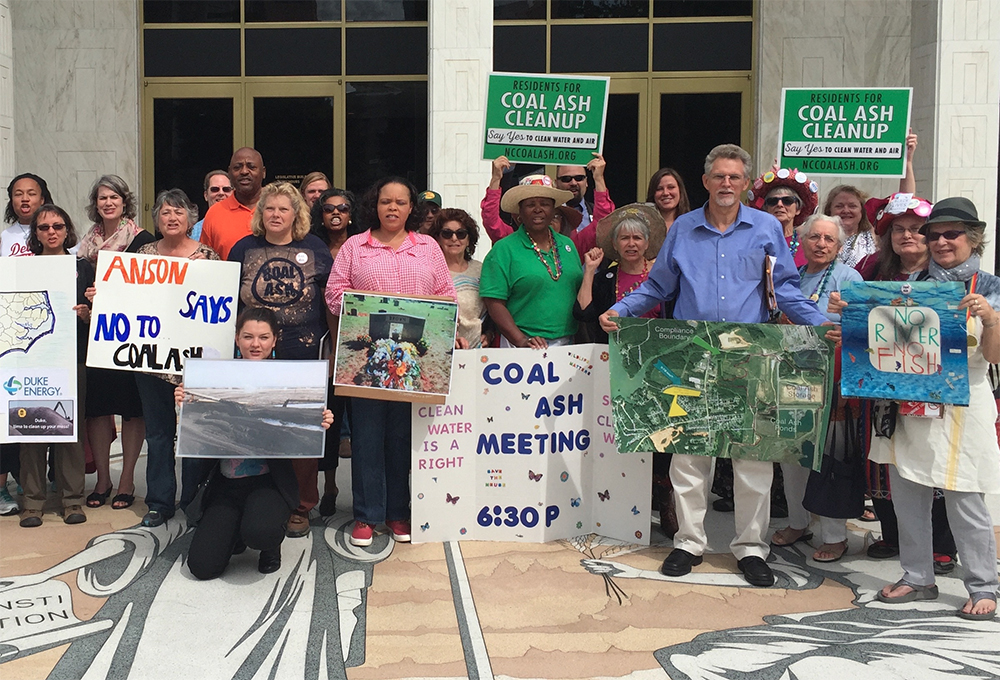
Citizens living near North Carolina’s 33 coal ash impoundments — all of which have leaked — have fought for transparency from Duke and the state, and for cleanup of the pollution that threatens their property value, health and family. Their actions forced this issue into the headlines of news networks and to the forefront of environmental justice conversations in the United States.
Appalachian Voices stood with these communities as we worked for years to compel Duke Energy and the N.C. Department of Environmental Quality to excavate coal ash from all the North Carolina sites and dispose of it either in lined, dry landfills, away from waterways, or by recycling it for concrete or other uses, provided it’s done in a manner that protects public health and the environment.
On Jan. 2, 2020, North Carolina announced a historic settlement with one of the state’s most powerful corporations and polluters, Duke Energy. The settlement requires Duke to move nearly 80 million tons of toxic coal ash at six of its power plants to properly lined landfills onsite or recycle it.

Learn information about specific coal ash impoundments in the South, including health threats and safety ratings:
Additional Resources
Fact sheets, videos, links to academic research, and more
Sign Up to Act
Help us protect the health of our communities and waterways.
Latest News
Sleeping giants: TVA and Georgia Power stuck in second gear on energy efficiency
While even the region’s top achievers have room for improvement, some of the largest utilities in the Southeast are seriously falling behind on energy efficiency. In particular, the Tennessee Valley Authority and Georgia Power are two enormously capable utilities that appear to be stuck in second gear.
Renewing the promise of Appalachia
There’s more than wildflowers budding in Appalachia as spring comes to the mountains this year. We are witnessing the proliferation of efforts big and small to stabilize and revitalize local economies as the coal industry declines. And the conversations continue expanding outward, bringing together an increasingly broad cross-section of residents and stakeholders.
Amber and Jimmy join the AV team
Amber Moodie-Dyer — North Carolina Energy Savings Outreach…
Dominion open houses bring communities together
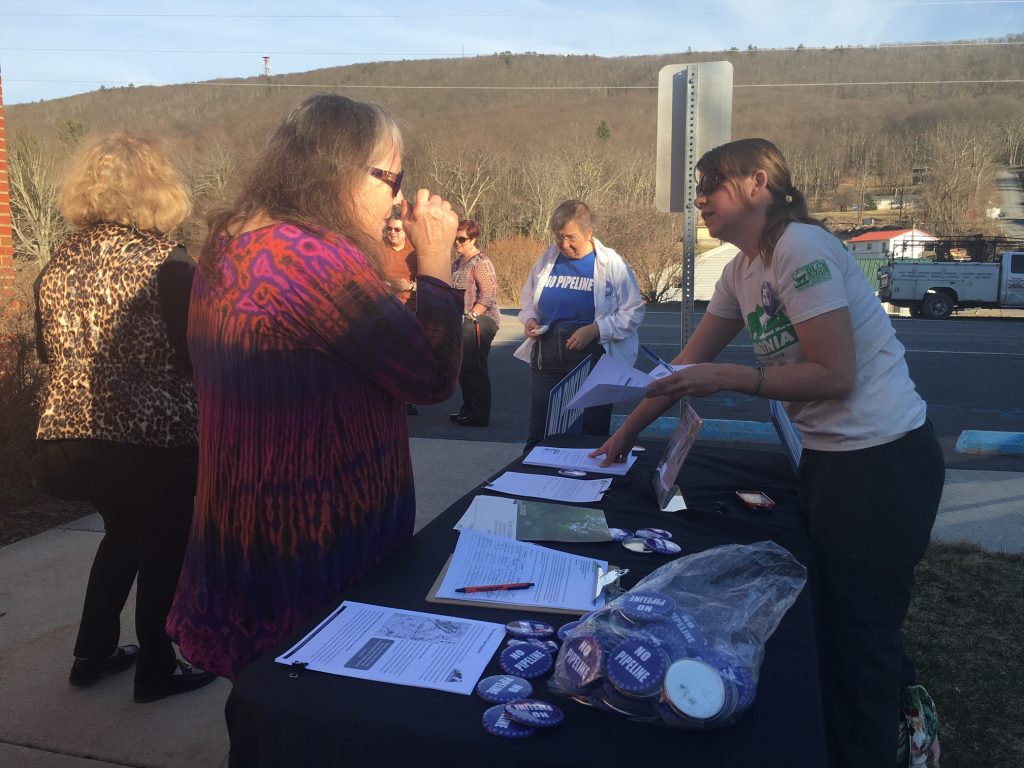
A pattern emerged during the recent trio of open house meetings hosted by Dominion on the proposed Atlantic Coast Pipeline in Churchville, Hot Springs and Snowshoe, Va. Unfortunately, it was a pattern of misleading materials, unhelpful spokespeople and dubious facts.
DEQ’s “Do Not Drink” reversal elevates coal ash concerns
State officials in North Carolina owe citizens an apology and an explanation. The state Department of Environmental Quality and Department of Health and Human Services are walking back their own recommendations that families living near coal ash ponds not drink or cook using well water containing levels of toxic substances that exceed their own standards.
DEQ flip-flops on drinking water safety
PRESS STATEMENT For immediate release, March 8, 2016…