Cleaning Up Coal Ash
For well over a century, power plants across the country have burned coal to generate electricity. And for just as long, leftover coal ash has been dumped in open, unlined pits near the power plant, usually located on a river or lake. Every year, U.S. power plants produce 130 million tons of coal ash, which is the second largest waste stream in the country after municipal garbage.
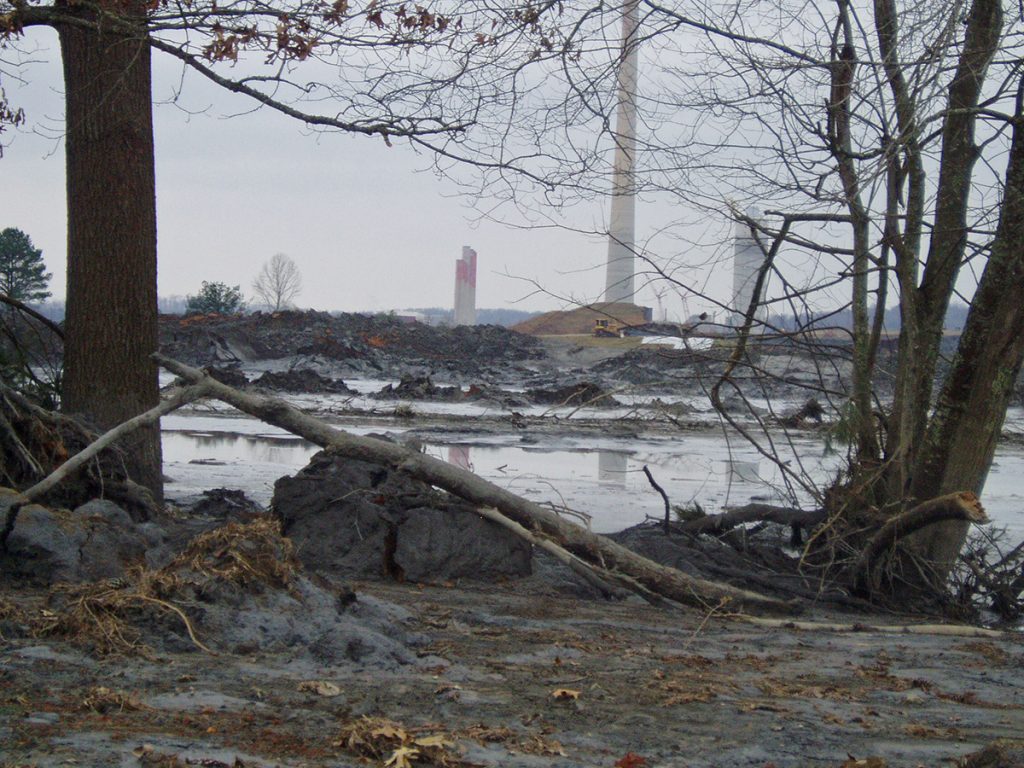
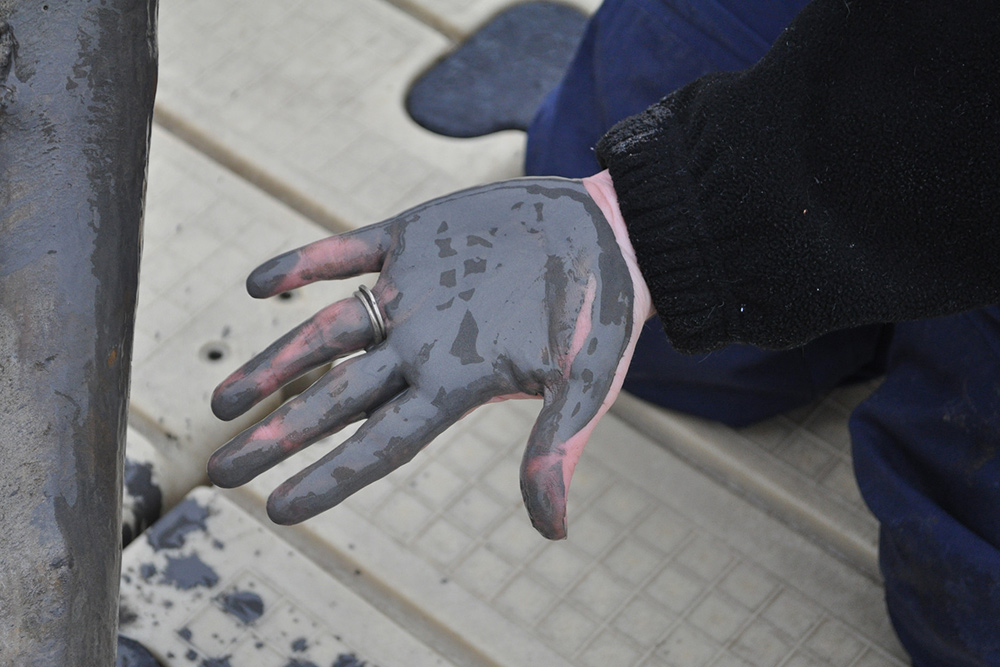
Coal ash concentrates the toxic heavy metals found in coal, including arsenic, mercury, lead and selenium. Stored in unlined, wet impoundments, coal ash has been leaking these toxics into our groundwater and surface waters for years. Sometimes these impoundments collapse — with disastrous results.
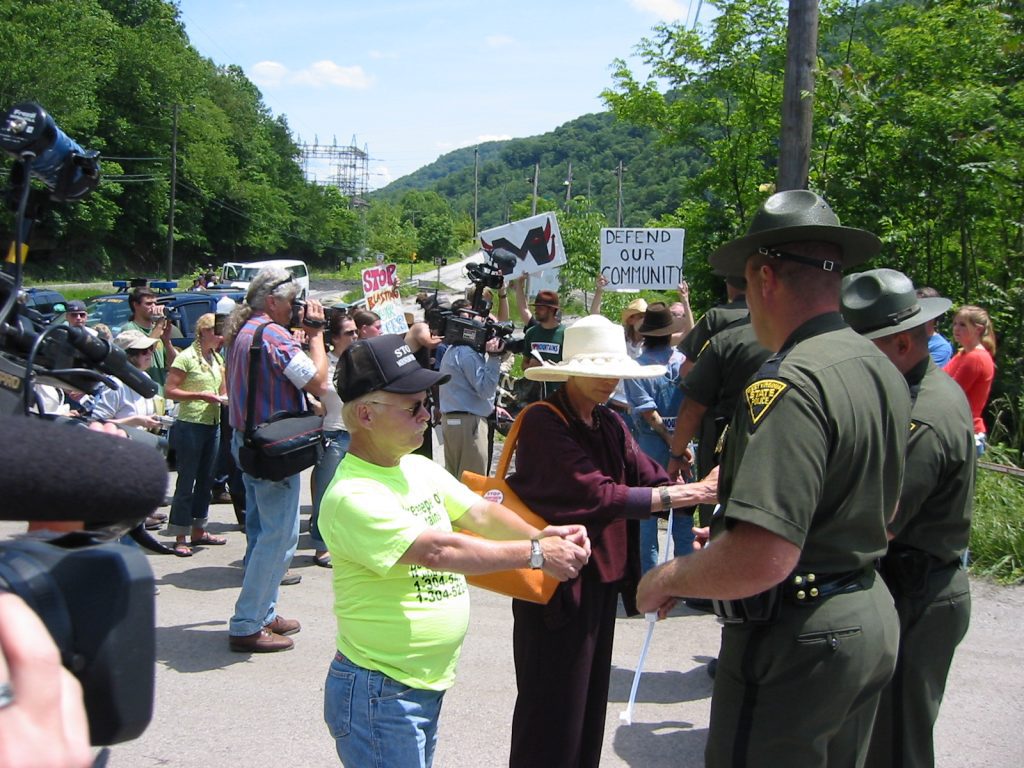
Yet government regulations for coal ash management are either non-existent or sparse, and there is little enforcement of the regulations that do exist. In North Carolina, this lack of oversight — and the complicity between state regulators, elected officials and Duke Energy — came to a boiling point in February 2014 when one of Duke’s coal ash impoundments spilled 39 million tons of ash into the Dan River.
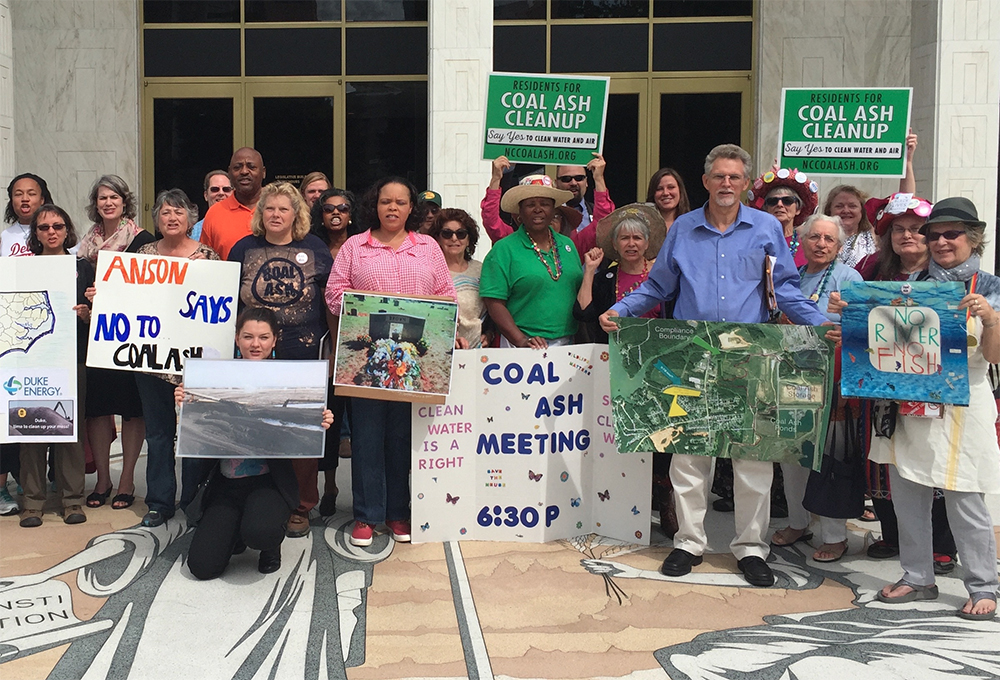
Citizens living near North Carolina’s 33 coal ash impoundments — all of which have leaked — have fought for transparency from Duke and the state, and for cleanup of the pollution that threatens their property value, health and family. Their actions forced this issue into the headlines of news networks and to the forefront of environmental justice conversations in the United States.
Appalachian Voices stood with these communities as we worked for years to compel Duke Energy and the N.C. Department of Environmental Quality to excavate coal ash from all the North Carolina sites and dispose of it either in lined, dry landfills, away from waterways, or by recycling it for concrete or other uses, provided it’s done in a manner that protects public health and the environment.
On Jan. 2, 2020, North Carolina announced a historic settlement with one of the state’s most powerful corporations and polluters, Duke Energy. The settlement requires Duke to move nearly 80 million tons of toxic coal ash at six of its power plants to properly lined landfills onsite or recycle it.

Learn information about specific coal ash impoundments in the South, including health threats and safety ratings:
Additional Resources
Fact sheets, videos, links to academic research, and more
Sign Up to Act
Help us protect the health of our communities and waterways.
Latest News
Funding must continue for Appalachian Regional Commission, urge government leaders and community groups
This week, more than 80 state and local government officials, educational institutions, businesses, churches and nonprofits sent a letter to members of Congress calling for sustained funding for the Appalachian Regional Commission.
On the Road to Recovery: Rebuilding the Virginia Creeper Trail
Hurricane Helene devastated part of the popular Virginia Creeper Trail. Despite promising recent updates, the timeline for major restoration and eventual completion for portions of the picturesque rail-to-trail path remains uncertain, requiring small businesses that rely on visitors to pivot or risk closure.
Appalachian Voices statement on Senate passage of H.R.1, slashing clean energy in favor of billionaire and polluter tax breaks
Today, the U.S. Senate passed the reconciliation bill, H.R. 1, officially known as the “One Big Beautiful Bill Act.” The bill will hinder new energy production and lead to an increase in electricity prices for the entire country by repealing energy efficiency and renewable energy tax credits, while creating a new tax credit for metallurgical coal production.
Research On Larry Gibson Dedicated To The West Virginia & Regional History Center
Marybeth Lorbiecki compiled 1,283 pages of research to produce a biography on Larry Gibson that was officially transferred in March to the West Virginia & Regional History Center at West Virginia University. Her research chronicles Gibson’s rise from an unknown working-class man into the international star he’d become for environmental activists.
Clinchco community meeting on energy resilience
This July, the town of Clinchco and Appalachian Voices are hosting a community meeting to inform energy backup planning in the area. The community meeting will be open to the public and will take place on July 15 at 5:30 p.m. at the Clinchco Senior Citizens Center.
Nonprofits, Tribes and local governments sue Trump administration for terminating EPA grant programs
Today, a coalition of nonprofits, Tribes and local governments sued the Trump administration for unlawfully terminating the Environmental Protection Agency’s Environmental and Climate Justice Block Grant Program despite a congressional directive to fund it.