Cleaning Up Coal Ash
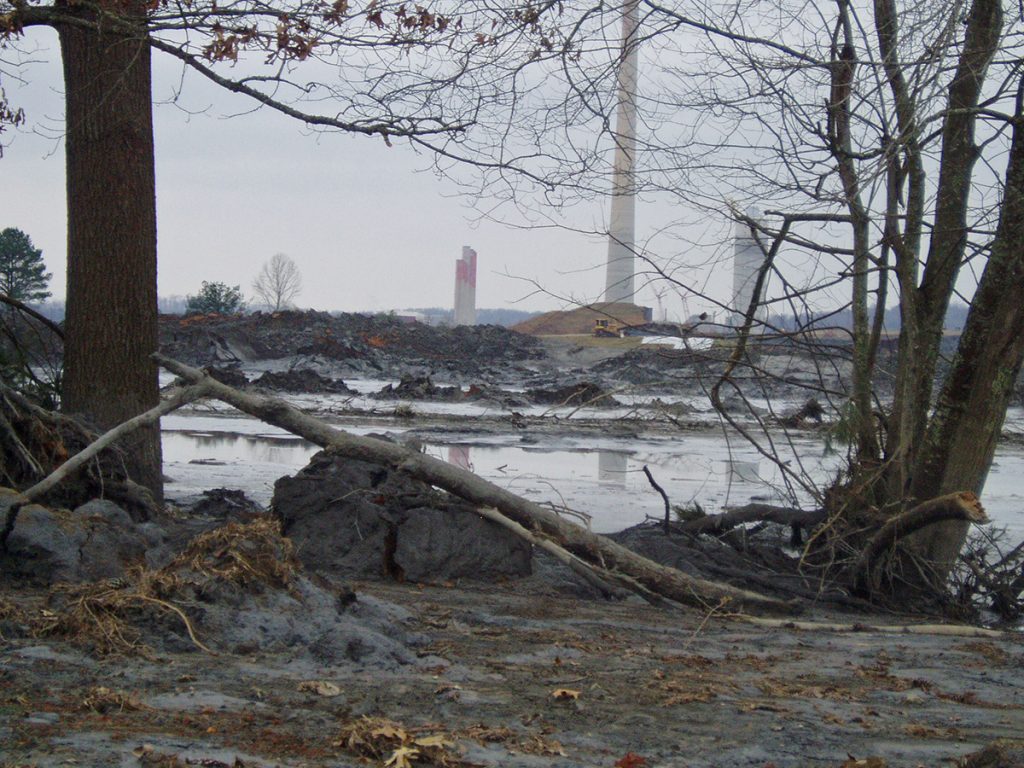
For well over a century, power plants across the country have burned coal to generate electricity. And for just as long, leftover coal ash has been dumped in open, unlined pits near the power plant, usually located on a river or lake. Every year, U.S. power plants produce 130 million tons of coal ash, which is the second largest waste stream in the country after municipal garbage.
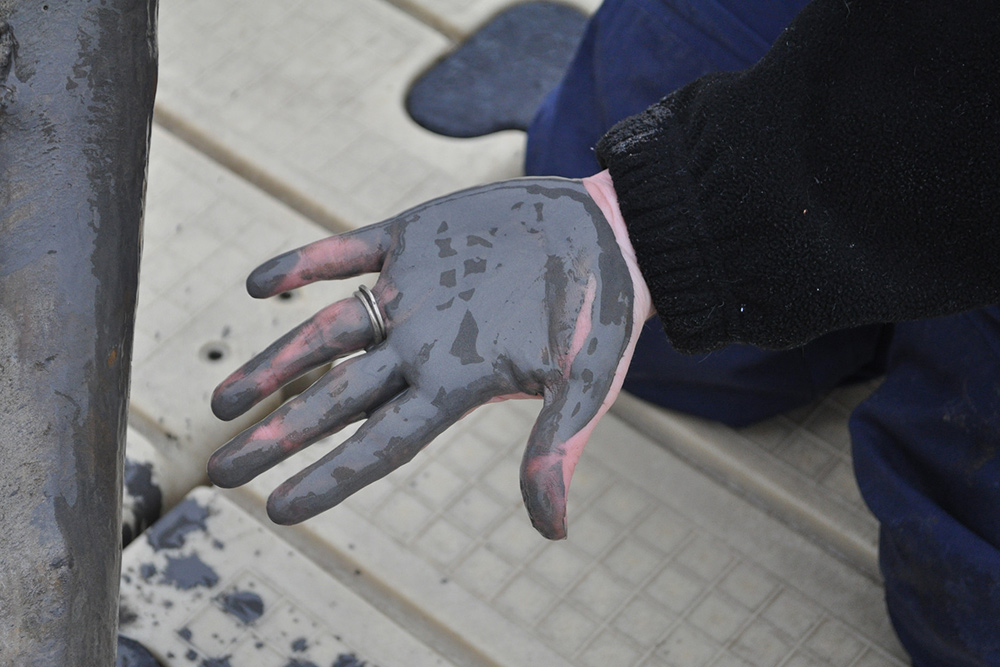
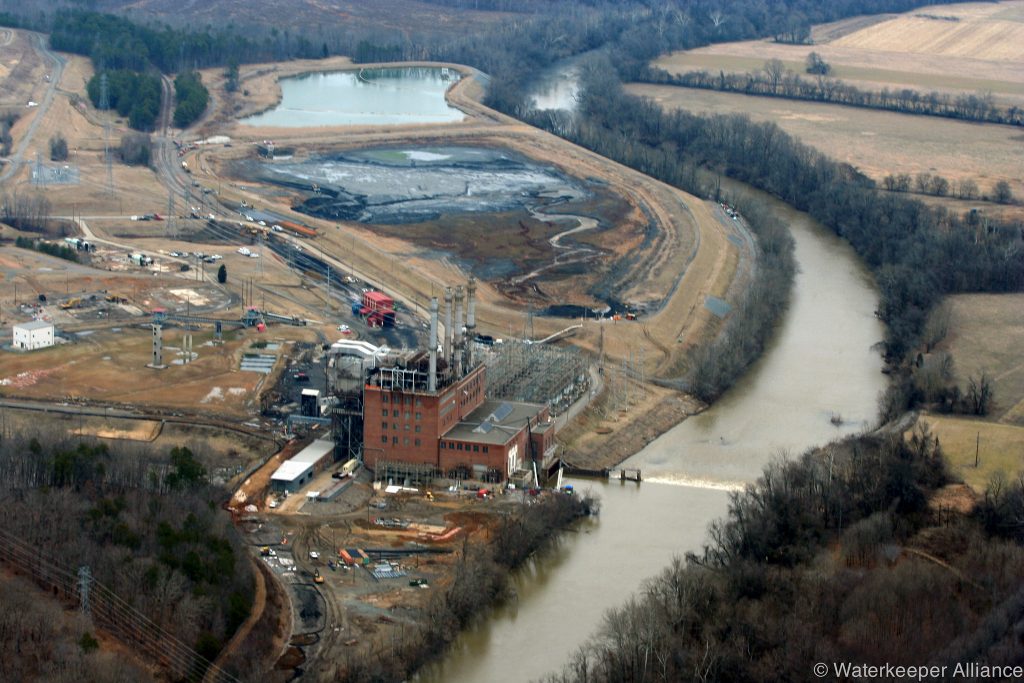
Coal ash concentrates the toxic heavy metals found in coal, including arsenic, mercury, lead and selenium. Stored in unlined, wet impoundments, coal ash has been leaking these toxics into our groundwater and surface waters for years. Sometimes these impoundments collapse — with disastrous results.
Yet government regulations for coal ash management are either non-existent or sparse, and there is little enforcement of the regulations that do exist. In North Carolina, this lack of oversight — and the complicity between state regulators, elected officials and Duke Energy — came to a boiling point in February 2014 when one of Duke’s coal ash impoundments spilled 39 million tons of ash into the Dan River.
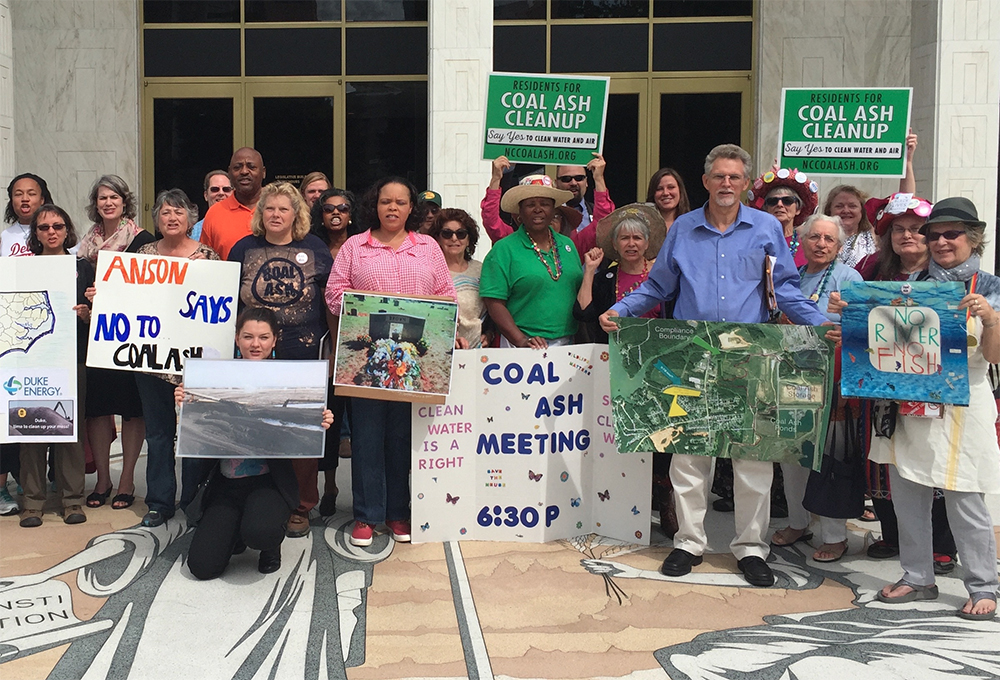
Citizens living near North Carolina’s 33 coal ash impoundments — all of which have leaked — have fought for transparency from Duke and the state, and for cleanup of the pollution that threatens their property value, health and family. Their actions forced this issue into the headlines of news networks and to the forefront of environmental justice conversations in the United States.
Appalachian Voices stood with these communities as we worked for years to compel Duke Energy and the N.C. Department of Environmental Quality to excavate coal ash from all the North Carolina sites and dispose of it either in lined, dry landfills, away from waterways, or by recycling it for concrete or other uses, provided it’s done in a manner that protects public health and the environment.
On Jan. 2, 2020, North Carolina announced a historic settlement with one of the state’s most powerful corporations and polluters, Duke Energy. The settlement requires Duke to move nearly 80 million tons of toxic coal ash at six of its power plants to properly lined landfills onsite or recycle it.

Learn information about specific coal ash impoundments in the South, including health threats and safety ratings:
Additional Resources
Fact sheets, videos, links to academic research, and more
Sign Up to Act
Help us protect the health of our communities and waterways.
Latest News
Pushing back on Appalachian Power’s unfair solar restrictions for schools and governments
Appalachian Power Company is blocking local schools and municipal governments from installing solar. But these public entities have the opportunity to strike a better deal during upcoming contract negotiations with the obstructionist utility.
43,000 demand FERC reject extended permit for Mountain Valley Pipeline
CONTACT: Doug Jackson, 202-495-3045, doug.jackson@sierraclub.org Cat McCue, 434-293-6373,…
Snorkeler Casper Cox Explores Appalachia’s Diverse Freshwater Life
Snorkeling Appalachia’s rivers and creeks puts adventurers face-to-face with a diverse and colorful array of fish.
EPA Finalizes Weakened Coal Ash Rule
The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency’s new rule allows utilities to dump coal ash into unlined pits through April 2021, and some companies may be able to do so for longer.
Tennessee Adds Seven Sites to National Register of Historic Places
Four of the sites added by the Tennessee Historical Commission are in the Appalachian region.
“Succession School” to Help Ohio’s Elder Generation of Farmers
Young farmers can have trouble accessing land, and often the direct descendants of older farmers are becoming less interested in taking up the torch. An Ohio program aims to help older farmers with the succession process.