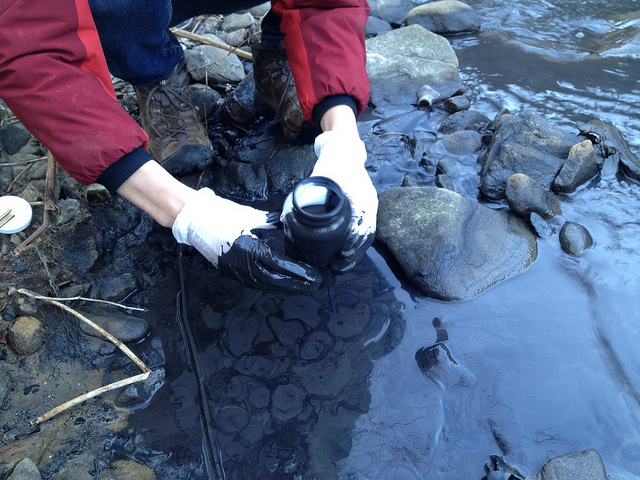
Holding the Coal Industry Accountable

An abandoned and decaying structure at the Sugar Cove Mine in Virginia. Photo courtesy of DMME
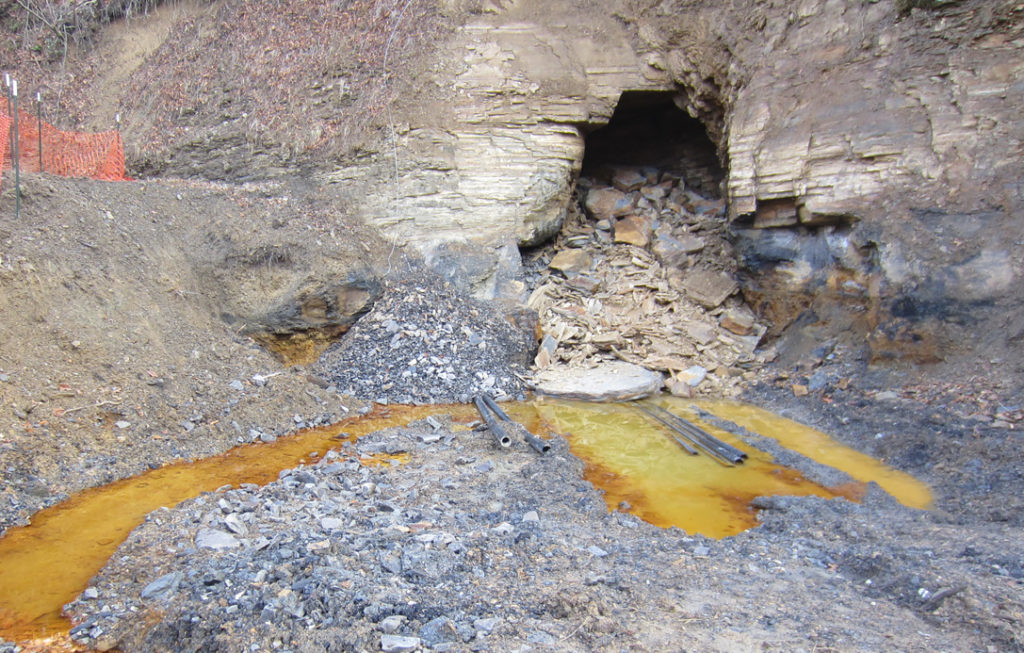
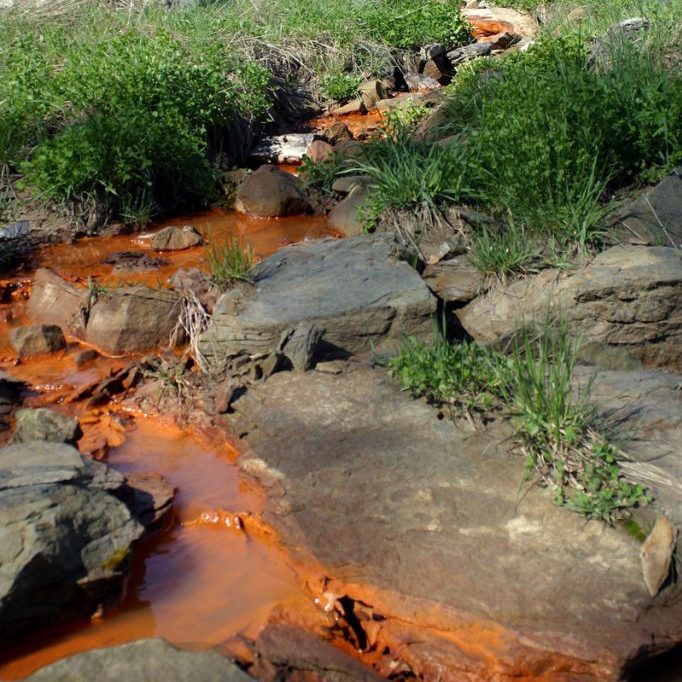
Centuries of coal mining in Appalachia have left a wake of destruction behind. Thousands of former mine sites still pose health and safety risks, and the extensive environmental damage includes polluted waterways, compromised groundwater, and the loss of 1.5 million acres of forest in one the most biologically diverse temperate ecosystems on the planet.
Residents in this region have dealt with increased illness and shortened life expectancy. Black lung disease is again on the rise, and both current and former miners are fighting to protect their vital healthcare benefits. Communities that depended on the coal industry’s boom years now face daunting financial challenges.
Meanwhile, the bosses and bankers who got rich off of Appalachia realize that the market for coal is continuing to decline. Many are trying to jump ship, taking their wealth with them and leaving the problems for local communities and taxpayers to deal with.

As Appalachian Voices continues to fight new mountaintop removal coal mining permits and monitor existing mines, we are also committed to ensuring that the communities that have long borne the brunt of mining are not left behind. We are determined to hold the coal profiteers responsible for cleaning up the land and water they defiled and fulfilling their obligations to miners and their families.
Communities near mines and power plants are among those that often face elevated air pollution. We’re working with 16 community groups and two universities to track air quality in communities throughout Kentucky, Pennsylvania, Tennessee, Virginia and West Virginia with about 80 monitoring devices. These are deployed at in communities near fossil fuel infrastructure and other industries.
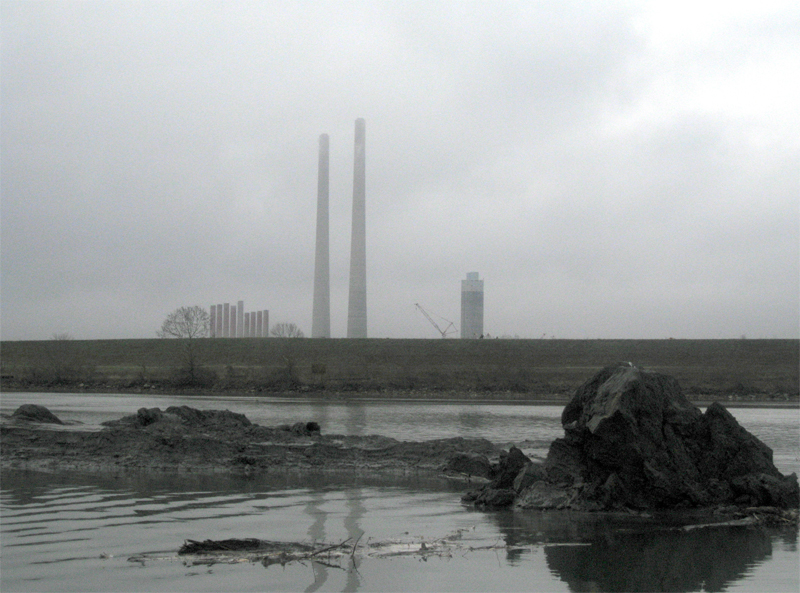
Similarly, the communities living near coal-fired power plants have suffered the burden of air and water pollution created by burning coal for electricity. Our years-long campaign alongside North Carolina communities impacted by Duke Energy’s dangerous storage of coal ash resulted in statewide cleanup orders, and we are committed to making sure the massive utility follows these rules.
We’re also working with communities in East Tennessee, site of the first major coal ash disaster in the country, to ensure that coal ash is stored in ways that protect residents, workers and waterways. And we’re engaged in legal challenges against Trump-era rollbacks on federal regulations for coal ash handling.
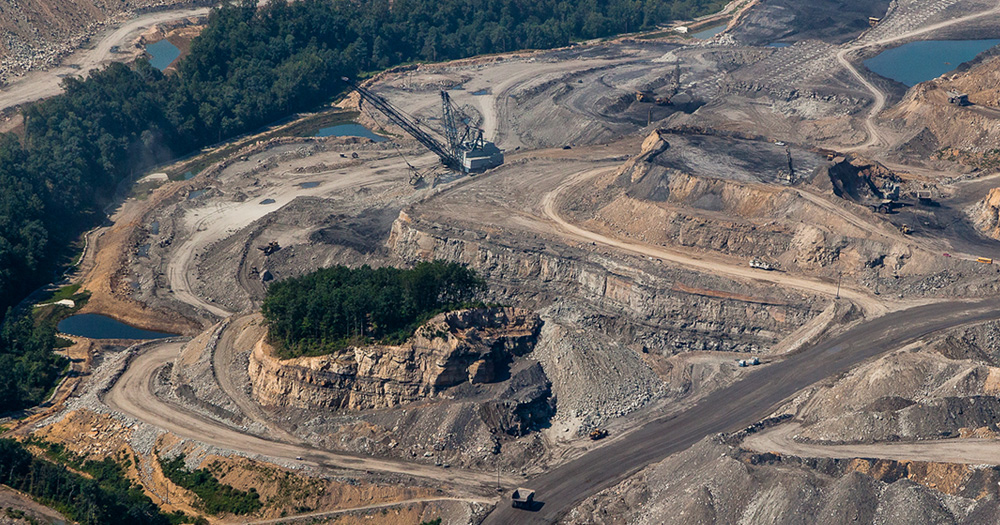

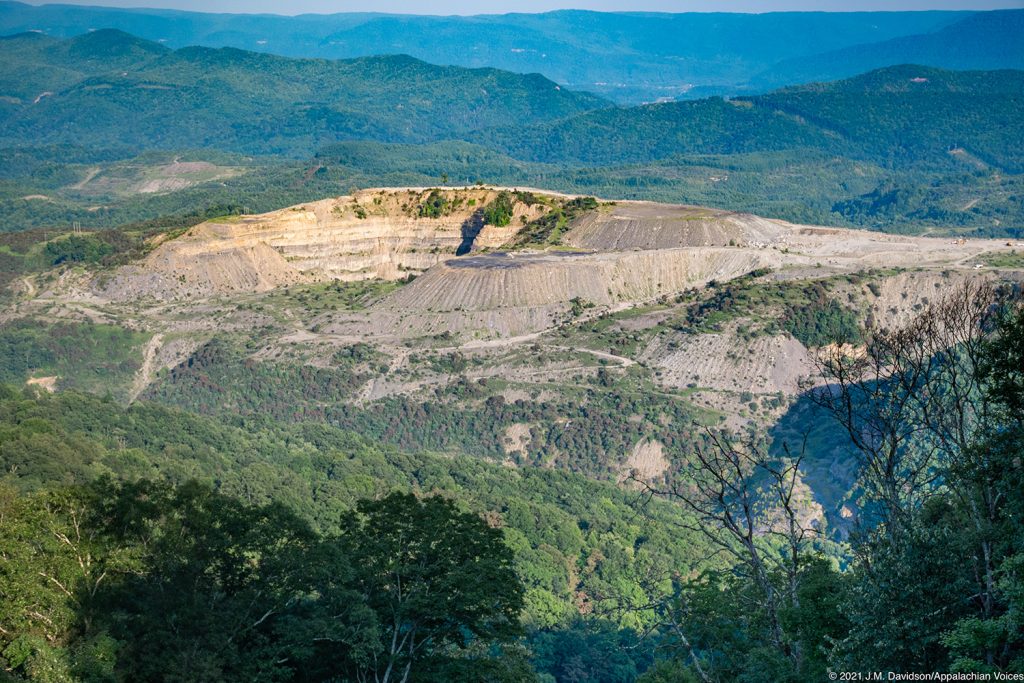
Ending Mountaintop Removal
Since the 1970s, the coal industry has blown up more than 500 of the oldest, most biologically rich mountains in America and destroyed more than 2,000 miles of headwater streams. Despite an ongoing citizen movement to end the destruction, and despite the decline in coal, it’s still happening.
Protect coal miners: Oppose cuts to NIOSH and MSHA
Black lung disease continues to ravage coal mining communities, despite regulations that are supposed to make their job safer. Unfortunately, the federal agencies that provide essential health services to miners are facing cuts.

Latest News
Clean Water Laws Wrestle With Coal
America’s environmental regulations have hampered the coal industry to varying degrees for decades, and though those rules can protect communities from pollution, the law alone is often not able to secure clean water. Here are some of the trouble spots.
In the Neighborhood: Living with Coal Ash
By Sandra Diaz Tracey Edwards, a lifelong resident…
Contaminated Drinking Wells Near Ash Ponds
As of July, the N.C. health department sent “do not drink” notices to 301 homeowners near coal ash ponds whose well water contains dangerous levels of heavy metals and other contaminants associated with coal ash.
Statewide Alliance Forms to Address Coal Ash in N.C.
On Saturday, July 25, Appalachian Voices and several of our partner organizations facilitated the first statewide gathering of North Carolina communities impacted by coal ash.
“It’s just vitamins!” Industry confuses residents on coal ash safety
Duke Energy and the N.C. Department of Environment and Natural Resources continue to confound and confuse families that have the unfortunate luck of living in close proximity to the utility’s coal ash lagoons. So citizens and county officials are stepping in to help residents air their frustrations and, hopefully, to receive some answers.