Front Porch Blog
Updates from Appalachia

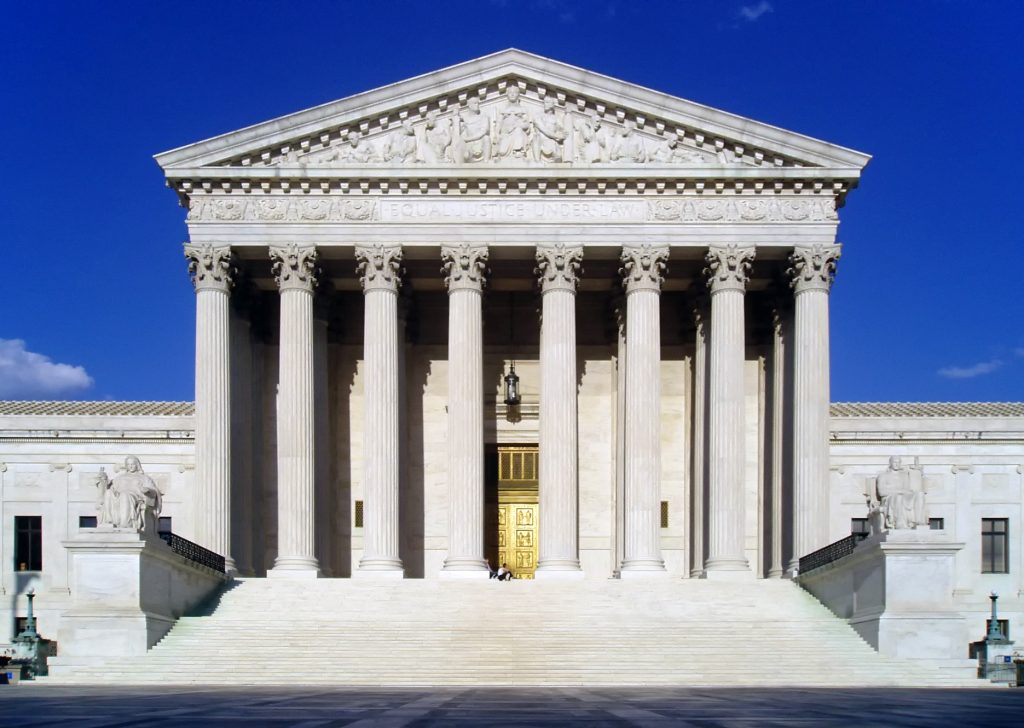
SCOTUS pauses the Clean Power Plan, for now
After a setback dealt by the U.S. Supreme Court, it’s imperative that decision makers in our region understand the opportunities presented by the Clean Power Plan rather than falsely attacking it as the cause of the coal industry’s hard times.
POWER+ Plan has a place in Obama’s final budget
This morning, President Obama sent his plan for the federal government’s expenses during fiscal year 2017 to Congress. It lays out the president’s vision for spending on everything from clean energy to cancer research. We’re happy to announce that the POWER+ Plan is included.
Action needed: Va. General Assembly considers pipeline policy fixes
Late last month, we learned that the U.S. Forest Service rejected the Atlantic Coast Pipeline’s proposed route. This development significantly checks the lickety-split pace of the project. If that renews your desire to take action, there are opportunities channel that feeling into these important legislative fights in the General Assembly.
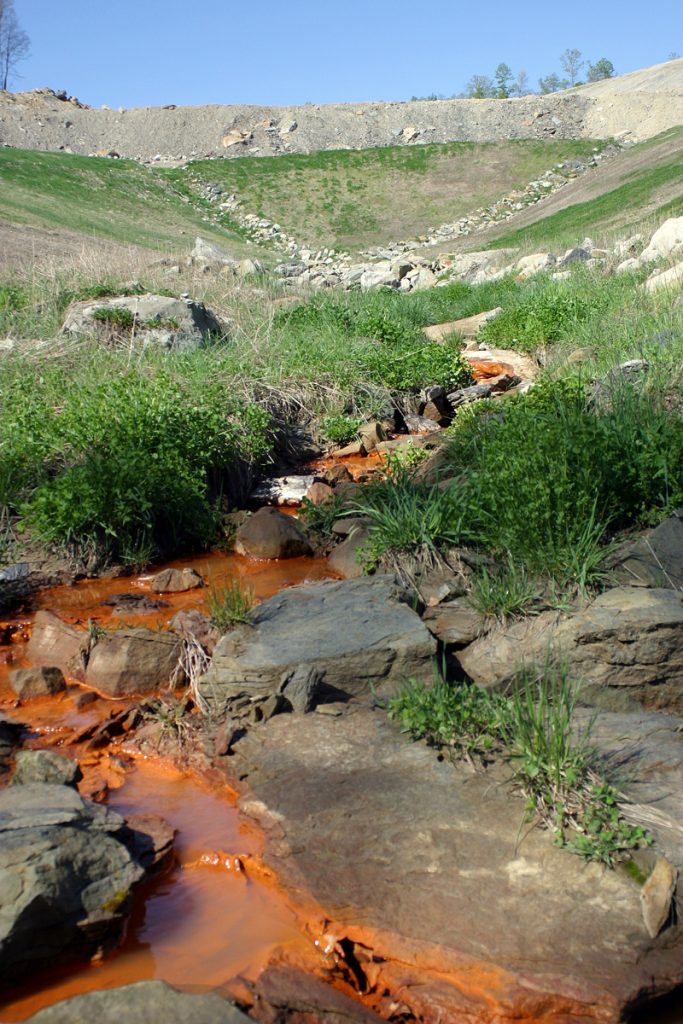
Appalachia’s stream health in the balance
“I can remember swimming, fishing, and camping on the Powell River. I can also remember times when those activities were not possible due to mining in the Powell River’s watershed that had devastated the ecosystem, wiping out fish populations and polluting the water to the point that it was unhealthy to swim in. My hope is that the Stream Protection Rule will ensure our rivers and streams are healthy for all the life that depends on them – including us.” — Adam Malle’s testimony to OSMRE on the Stream Protection Rule
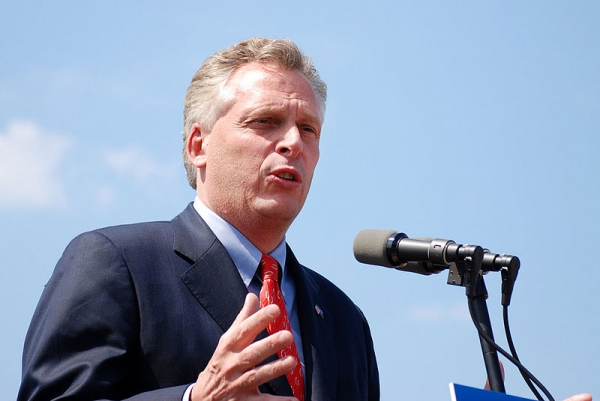
Va. leaders urge Gov. McAuliffe to reject Dominion’s climate-polluting plan
From Appalachian Voices’ Press Room: Earlier this week, a wide array of Virginia leaders released a letter asking Governor Terry McAuliffe to reject efforts by Dominion Power that would increase carbon pollution in the Commonwealth.